Understanding RTK and Its Importance in Automotive Testing with ADMA Systems
What is RTK?
RTK, or Real-Time Kinematic positioning, is a satellite navigation technique that enhances the precision of GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System) signals. Unlike standard GNSS, which typically offers accuracy within several meters, RTK can achieve centimeter-level precision by using correction data from a fixed base station or a network of reference stations.
This requires:
- A base station that knows its exact location.
- A rover unit (e.g., a vehicle-mounted GNSS receiver) that receives both satellite signals and correction data from the base.
- A communication link (radio, NTRIP over IP, or serial) between base and rover.
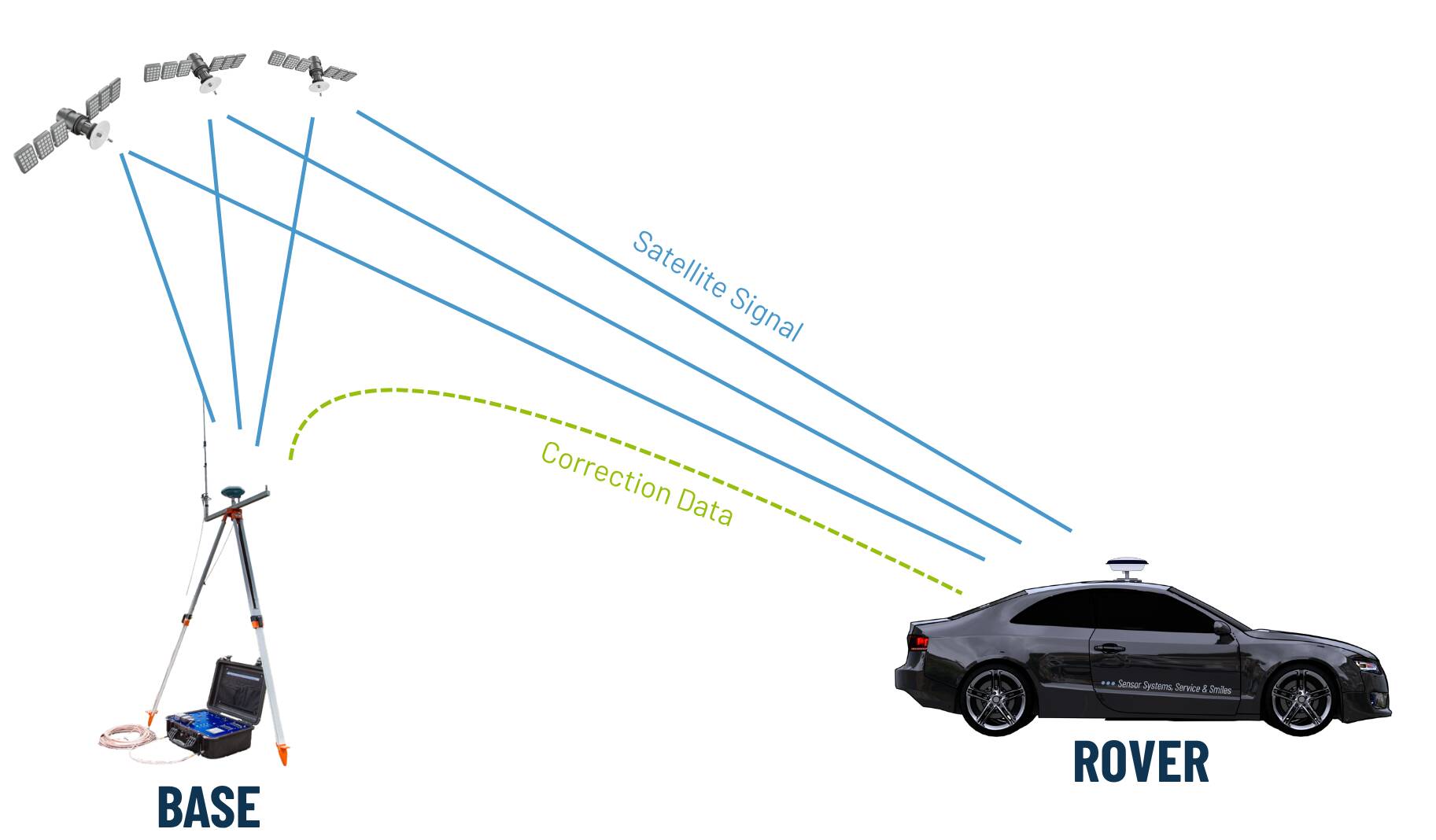
How RTK Works
RTK (Real-Time Kinematic) improves GNSS positioning accuracy from meters down to centimeters by using carrier phase measurements instead of just the code-based distances (called pseudoranges).
Normally, GNSS receivers calculate their position based on how long it takes for the satellite signal to reach them – this gives a distance with meter-level accuracy. RTK goes further: it also measures the carrier phase of the satellite signal, which has a much shorter wavelength and is therefore much more precise.
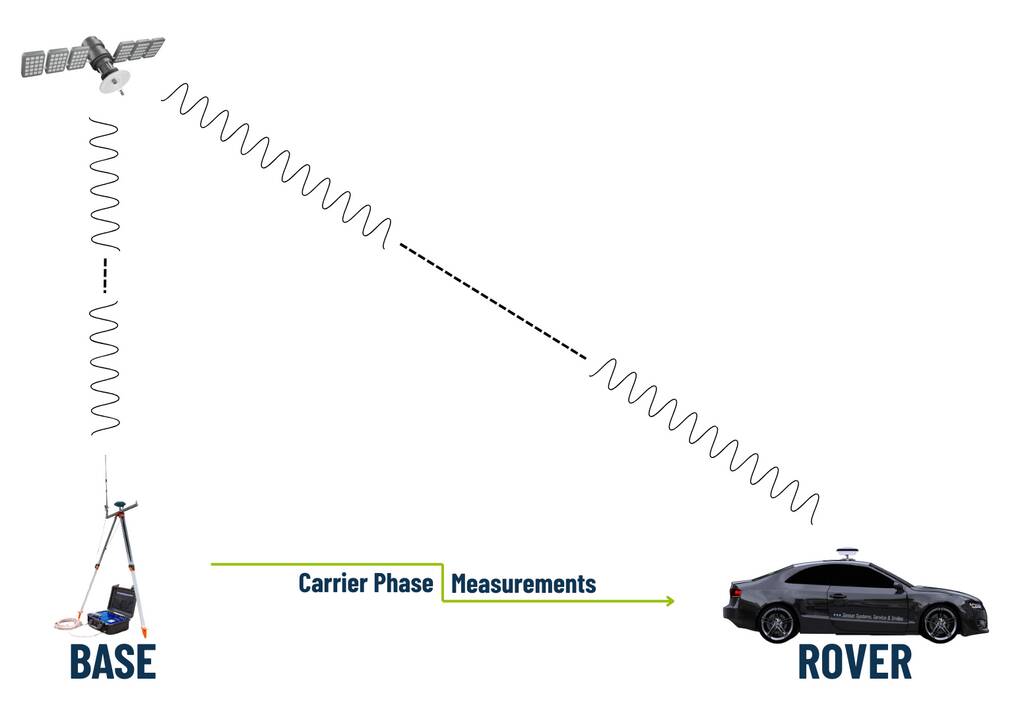
However, there’s a challenge – the receiver doesn’t know how many whole wavelengths fit between the satellite and itself. This unknown number is called the integer ambiguity.
By resolving (or “fixing”) these integer ambiguities with correction data by a local base station, RTK can determine the exact number of wavelengths and achieve centimeter-level accuracy.
Summary
- The base station receives GNSS signals and compares them to its known position.
- It calculates the error and sends correction data to the rover.
- The rover applies these corrections in real time, achieving centimeter-level accuracy.
RTK can be delivered via:
- NTRIP client for reception from a NTRIP Provider
- NTRIP Modem for reception from a NTRIP Provider
- Radio modem for reception of a local base station
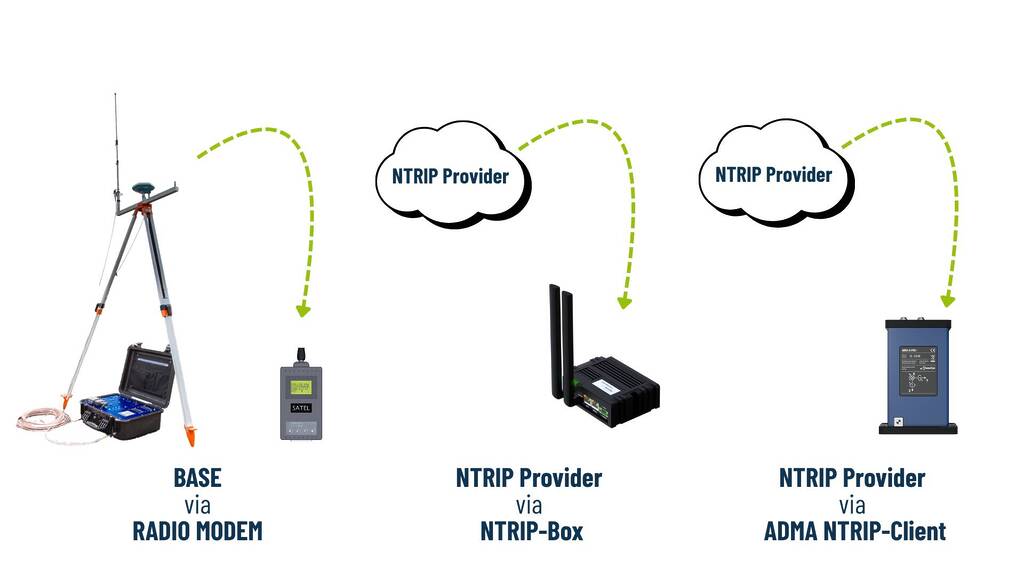
Regardless of the correction data source used, the standard format for correction data is RTCM messages. The current version in use is RTCM v3.2, which provides all essential information required for correcting up to four different GNSS signals: GPS, GLONASS, GALILEO, and BEIDOU. The ADMA system utilizes the MSM5 (Multiple Signal Message type 5) standard, which ensures compatibility and comprehensive support for multi-constellation GNSS corrections.
Koordinatensystem (WGS84, ETRS89, …)
When using a local base station whose position was determined by averaging GNSS observations, the base coordinates are typically expressed in the WGS84 coordinate system.
In contrast, regional NTRIP providers (for example, correction services operated by national mapping agencies) usually provide corrections referenced to the regional reference frame that is officially valid in their area. In Europe, this is typically ETRS89 (European Terrestrial Reference System 1989), which is aligned with the Eurasian tectonic plate and therefore accounts for continental drift relative to WGS84.
If you collect rover measurements in WGS84 and then combine or compare them with data in ETRS89, you will observe a position offset between the two datasets. This offset increases slowly over time due to the continuous drift of the Eurasian plate (currently about 2–2.5 cm per year relative to WGS84).
Therefore, it is important to ensure that all GNSS data within a project or survey campaign are referenced consistently to the same coordinate reference system. Mixing WGS84 and ETRS89 positions can lead to systematic errors in the results.
Typical Accuracies
- Horizontal: approx. 1-2 cm
- Vertical: approx. 2-3 cm
Requirements for this accuracy
- Good GNSS Coverage (≥ 6 valid satellites)
- Correction data in real time
- Max. Distance to Base station (< 15 km)
- Open sky conditions (No shadowing, no multipath)
Why RTK Matters in Automotive Applications
In modern automotive testing, especially for ADAS (Advanced Driver Assistance Systems) and autonomous driving, precise positioning is critical.
RTK enables:
- Accurate lane-level navigation.
- Reliable path-following tests.
- Precise measurement of braking distances, tire behavior, and vehicle dynamics.
RTK is particularly valuable in real-world driving scenarios, where vehicles must maintain exact trajectories and respond to environmental cues with minimal error.

ADMA and RTK: A Powerful Combination
The ADMA (Automotive Dynamic Motion Analyzer) system by GeneSys Elektronik GmbH is a GNSS-aided inertial measurement unit (IMU) designed for high-precision vehicle testing. It combines:
- Inertial sensors (accelerometers and gyroscopes)
- GNSS-Receiver
- Kalman filter algorithms for sensor fusion

When paired with RTK correction data, ADMA systems can deliver:
- Real-time 3D motion tracking
- Highly Precise yaw, pitch, roll, and side-slip angle measurements
- Accurate data even during GNSS outages, thanks to inertial backup
- Robust performance at high shocks due to the ASD (Advanced Standstill Detection)

With the ADMA-PP post-processing software it is possible to use these RTK correction data offline (after the test drive) as RINEX data. This enables you to use RTK even in regions with no mobile network connection.




