This operating configuration constitutes the most advanced system stage providing the best possible performance. A determination of absolute positions with (D)GNSS allows the most accurate inertial measurement to be performed.
Should the reception of the (D)GNSS data be interrupted, position measurement is performed by the ADMA without external augmentation (pure INS operation). On re-entry of valid (D)GNSS data the ADMA takes up GNSS/INS operation again.
The “Extended Kalman filter” used in the ADMA software can estimate, if system data is augmented with (D)GNSS, several important INS sensor errors, thus enhancing ADMA system performance, especially during GNSS outages.
Depending on the capability of the GNSS-receiver the position accuracy ranges from standard-GNSS (several meters), SBAS corrected DGNSS data (sub meter), down to RTK2 position with an accuracy of 1 cm.
For DGNSS operation you either need your own Base Station with radio-modem or GPRS-data link, or access to special DGNSS-data services via GSM/GPRS-data link (like AXIO-NET or SAPOS in Germany).
In some cases, satellite based correction data (SBAS) can be a solution for the required accuracy, but because of rare usage, it plays a subordinate role and will be described at the end of the article.
DGNSS Systems
NTRIP provider
With a NTRIP-DGPS-Modem connected, the ADMA sends a GPGGA log (contains important positioning data) to the NTRIP provider. The provider takes these information and generates correction data for a virtual local base station according to the sent position data.
Please see the Technical Documentation of GeneSys DGNSS Box.
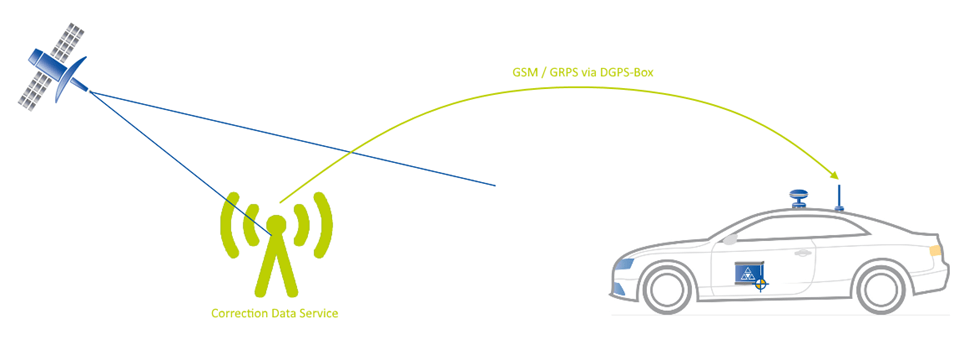
Local GNSS base station
By averaging the position over a long period of time, the GNSS base station is able to determine its exact position. With this absolute accurate position, the GNSS receiver of the base station is able to generate differen correction data formats and sends them via WLAN or a UHF radio modem.
Please see the Technical Documentation of GPS Base Station.

Wiring DGNSS

DGNSS correction data forwarding
The DGNSS correction data via Ethernet functionality allows to transmit correction data from one ADMA to another. By using the Ethernet broadcast function several ADMA systems can be provided. This functionality can reduce your workload and costs. For example, if you are performing an urban or interurban AEB test, now only one GPRS(NTRIP)-Box will be needed to provide RTK2 for multiple ADMA systems.
Note: For being authorized using DGNSS correction data via Ethernet a License is required. If a license is required, please contact GeneSys sales partner.

Setup and configuration
On menu 5️⃣ AUX SYSTEM/DGNSS Options you will find predefined DGNSS configurations for common use cases.
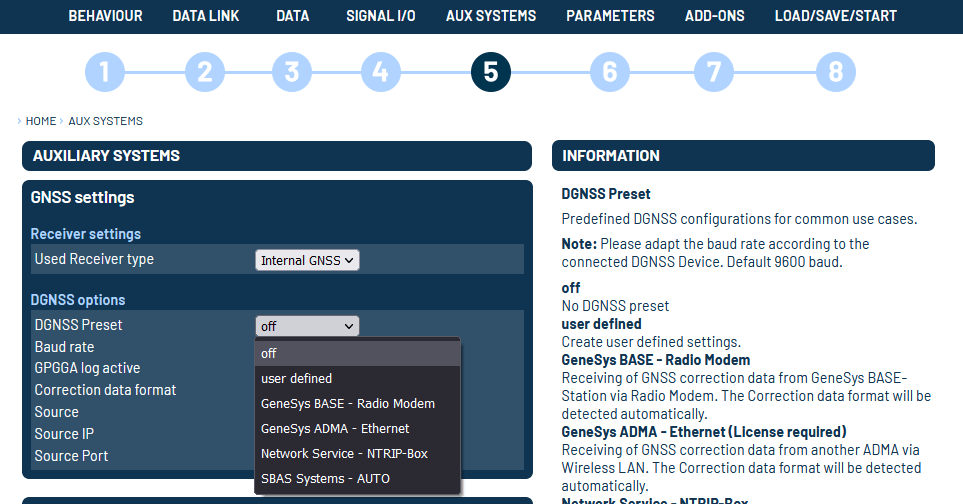
Available Presets
| PRESET | FUNCTION |
|---|---|
| Off | No DGNSS preset. |
| User defined | Create user defined settings. |
| GeneSys Base – Radio Modem | Receiving of GNSS correction data from GeneSys BASE-Station via Radio Modem. The Correction data format will be detected automatically. |
| GeneSys Base – GSM Modem | Receiving of GNSS correction data from GeneSys BASE-Station via GSM Modem. The Correction data format will be detected automatically. |
| GeneSys ADMA – Ethernet | Receiving of GNSS correction data from another ADMA via WLAN. The Correction data format will be detected automatically. (License required) |
| Network Service – NTRIP-Box | Receiving of GNSS correction data from correction data service via NTRIP-DGPS-Box over GSM or GPRS. The correction data format will be detected automatically. |
| SBAS System – Auto | Receiving of GNSS correction data from a satellite-based augmentation system (SBAS). The satellite system to be used is determined automatically. |
Satellite based GNSS correction data (SBAS)
With satellite based correction data (SBAS) the GNSS data accuracy can be improved. The satellites which are used transmitting the correction data. For this reason, signal coverage is only available in certain regions. It increases the positional accuracy of single GNSS (10 to 20 meters) to DGNSS (0,3 to 3 meters).

| SERVICE | DESCRIPRION | COUNTRY |
|---|---|---|
| WAAS | Wide Area Augmentation System | North America |
| EGNOS | European Geostationary Navigation Overlay Service | Europa |
| MSAS | Multifunctional Satellite Augmentation System | Japan |
| GAGAN | GPS-supported geo-enhanced navigation | India |
| QZSS | Quasi-Zenite Satellite System | Japan |
| WORK MODE | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| Auto | Automatically determines satellite system to use and prevents the receiver from using satellites outside of the service area. |
| Any | Uses any and all SBAS satellites found |
Use the DGNSS Preset user defined to activate this option on dialogue Auxiliary Systems.
Note: We don’t recommend using SBAS, because in case of Multi GNSS the receiver is only able to use one single GNS System, because he can only use one SBAS System at a time.


