The ADMA system offers various data streams that can be output through both CAN and Ethernet interfaces. Some streams are exclusively available via Ethernet and not through CAN.
Data Stream overview
The table below gives an overview of all available data streams and their output options:
| Data stream | Ethernet | CAN | Serial | License required |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ADMAnet | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | |
| Steering and driving robot | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ | |
| GNSS Raw data | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | (🔒) Can be sent via serial interface without license. |
| Add-On Braking | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | 🔒 |
| Add-On Delta 1:1 | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | 🔒 |
| Add-On Delta 1:5 | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ | 🔒 |
| Add-On LatDev | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | 🔒 |
| Target Ego | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ | |
| GPRMC | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | |
| GPGGA | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ |
Note: All data streams (except for the serial data streams) can be visualized and recorded in the ADMA Data Logger.
Ethernet (UDP) Output principle
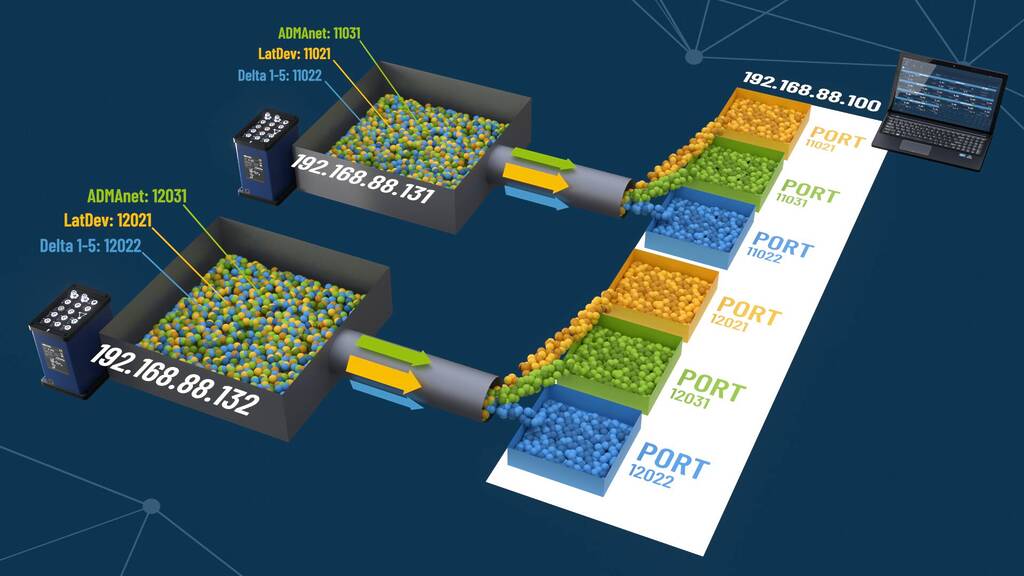
The following image shows a schematic of two ADMA systems in the same network, that output the same data streams to the same receiving device (DAQ).
The DAQ (Data Acquisition System) filters incoming UDP data packets by using source IP addresses and source ports. The source IP address identifies the system from which the data packet originates, while the source port determines the specific data stream. This allows the DAQ to correctly route the packets to the appropriate data stream reception container.
Configuration of the standard ethernet data streams
The settings for all license-free data streams can be found in the ADMA web interface under Menu 3 – Data. Here, they can be activated and configured.
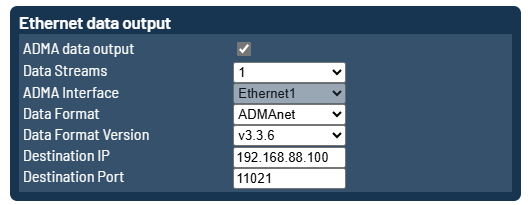
ADMAnet
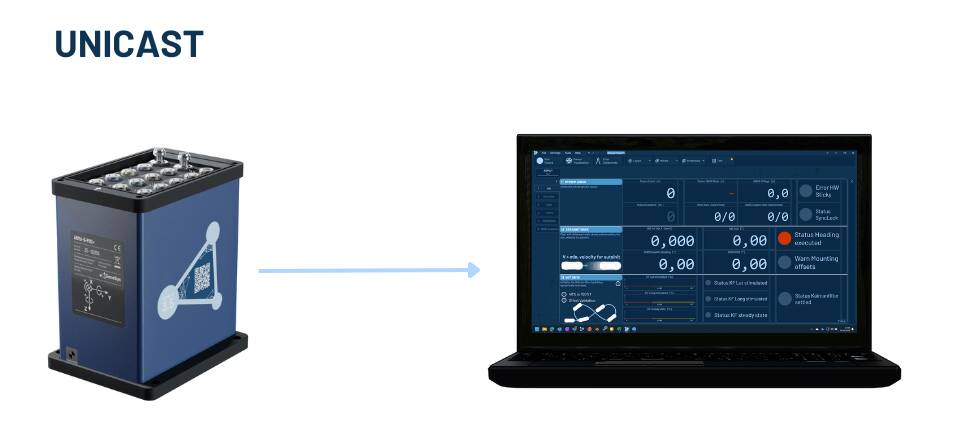
The ADMAnet data stream can be sent via unicast, what means directly to a speficif ip address.
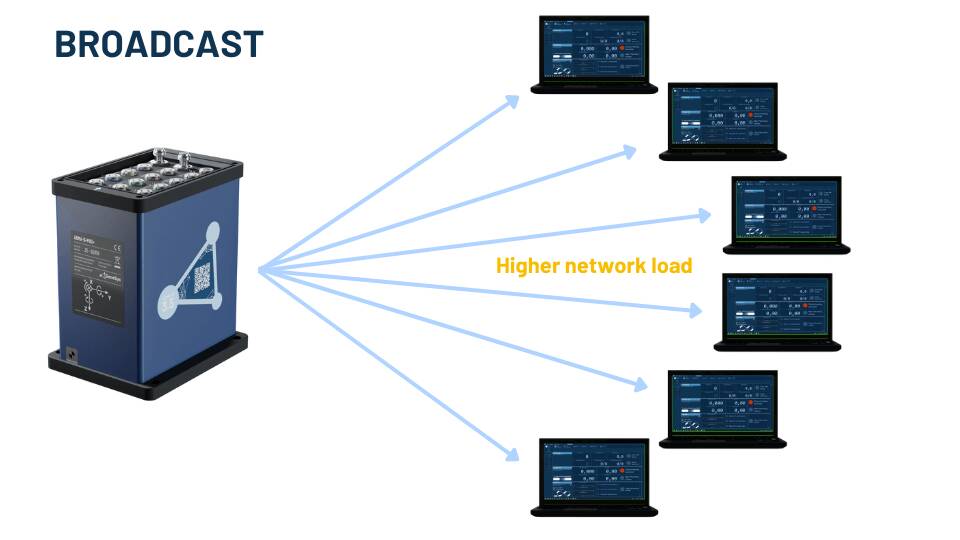
It is also possible to send it as broadcast, which results in a significantly higher network load.
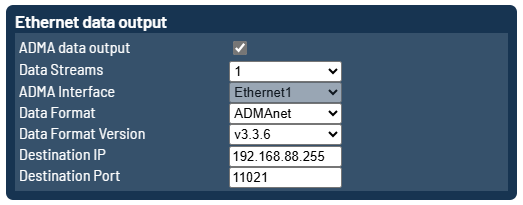
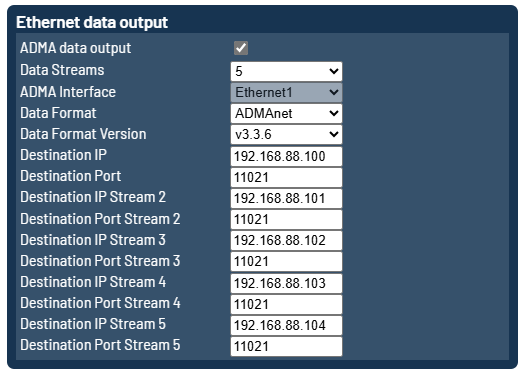
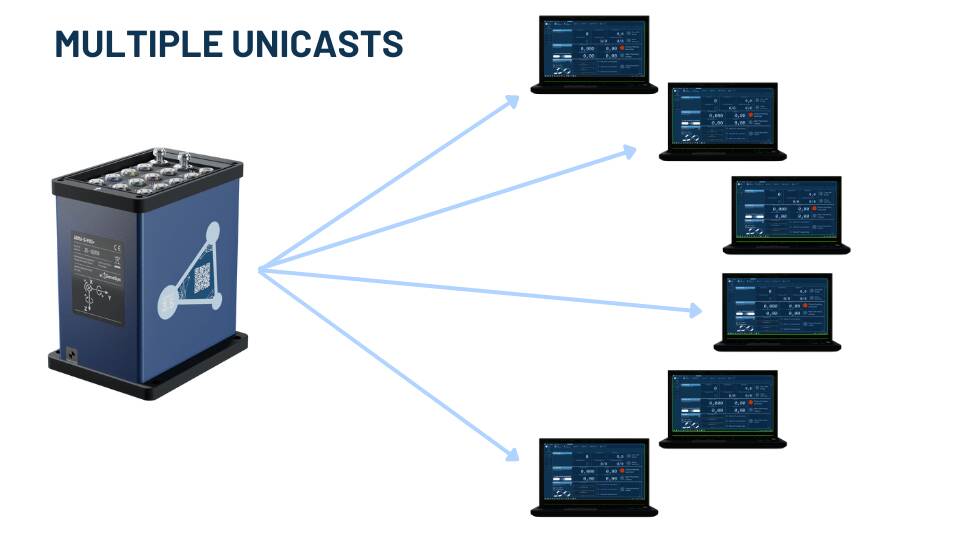
Additionally it is possible to send the ADMAnet data stream via multiple unicasts to up to five ip-addresses. This can be achieved by increasing the Data Streams setting.
Steering and driving robot data output
The robot data stream is used to provide position, movement and angle information to the robot system, so the robot is able to drive / steer the vehicle.
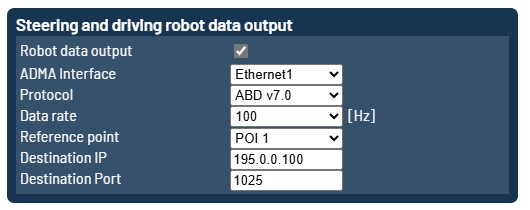
The robot data stream can be output through any Ethernet interface provided by your ADMA. The protocol must be selected based on the type of robot you are using. All POIs (Points of Interest) can be chosen as the reference point.
GNSS raw data output
The GNSS raw data stream is used for post processing or for later analysis of the GNSS signals.
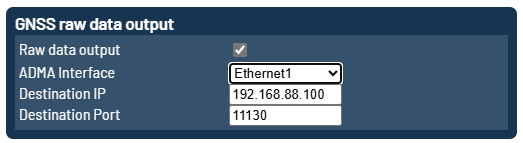
It can be output via Ethernet or via serial interfaces.
Configuration of the Add-On ethernet data streams
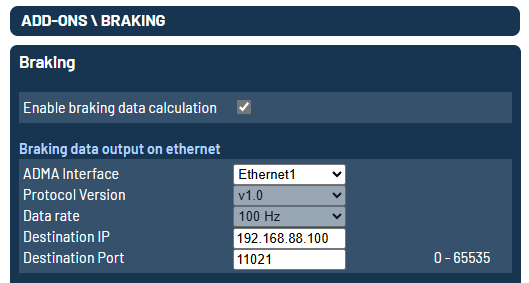
Add-On Braking
The Add-On Braking data stream can be activated at Add-Ons / Braking.
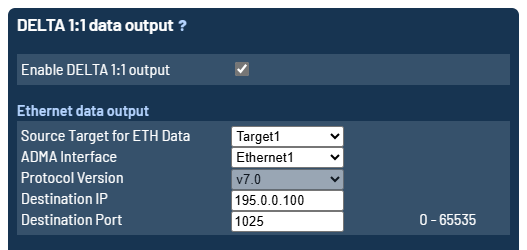
Add-On Delta 1:1
The Add-On Delta 1:1 data stream can be activated at the upper configuration page of Add-On / Delta 1:5 / Hunter Configuration of the ADMA webinterface. It is possible to select between the available ethernet interfaces.
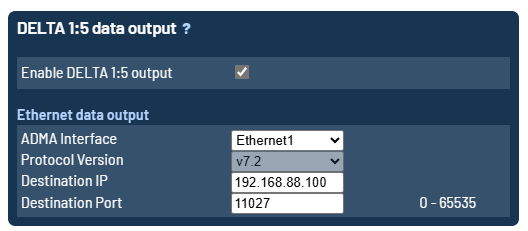
Add-On Delta 1:5
The Add-On Delta 1:5 data stream can be activated at the lower configuration page of Add-On / Delta 1:5 / Hunter Configuration of the ADMA webinterface. It is possible to select between the available ethernet interfaces.
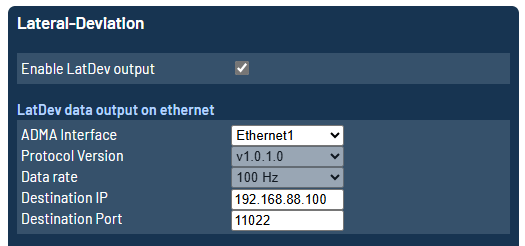
Add-On LatDev
The Add-On LatDev data stream can be activated at Add-Ons / Lateral-Deviation of the ADMA webinterface. It is possible to select between the available ethernet interfaces.
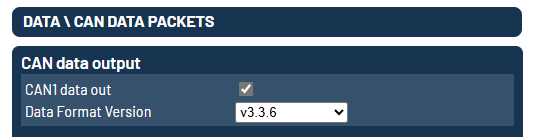
Configuration of the CAN data output
The CAN data output can be activated at 3 – Data / CAN data packets in the ADMA webinterface.
When activated, you have to select all data packets you want to output. This can be done in the following table.
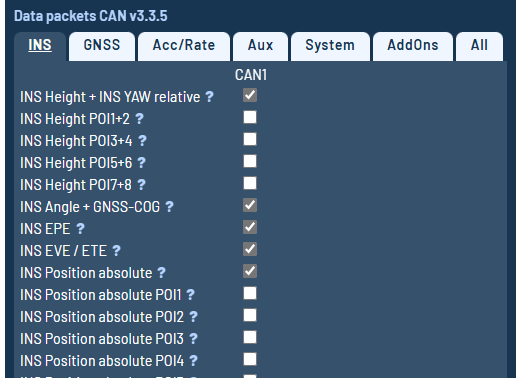
Note: The CAN data bus has bandwidth limits. Because of that you can only select a specific amount of data packets (depending on the selected update rate). Find more detailes at the article CAN output issues.

